With the rapid development of cloud computing and mobile Internet, the IT density and energy consumption increase sharply. No matter in mainland China or Hong Kong, or worldwide, the data center industry is faced with great pressure and challenges.
Seven defects of traditional data center
1. The data center CAPEX is staying high. With the rapid development of business, to construct a traditional data center needs to consider the future business growth rate. The initial investment is very large, but business grows phase by phase. This results in large initial investment and much waste of capacity.
2. The data center OPEX pressure is increasing. As is known to all, a data center consumes lots of energy. It has been the fifth largest energy-consuming industry, accounting for 2% of the total energy consumption of the society. The huge electricity bills have been sharply reducing the profit of enterprises which operate data centers. The electric charge accounts for 60% of a data center OPEX. Apart from huge electricity bills, a data center requires scheduled and unscheduled maintenance from a large number of professionals. Huge electric charge and complicated data centre maintenance increases the OPEX pressure.
3. The rigid construction mode cannot adapt to user needs. The Internet industry has been changing with an incredible speed. . Therefore, the construction of a data center must be agile. Clearly, the traditional construction mode with long construction period could not catch up with the fast speed of Internet development not agile.
4. The planning is difficult due to coupling of data center buildings and IT plans. The biggest difficulty for designing a data center for Internet is that the design requirements keep changing. The construction planning and design cannot catch up with IT development and change rate.
5. Risk control is difficult. The traditional mode relies on engineering. Made to order and construction on site are common. The technological level and professional quality of different construction teams vary wildly. The onsite quality is difficult to control.
6. Site management is difficult due to interweaving of different subject areas. The types of work involved in a data center are various. At least 12 professional fields are involved. The cooperation between different professional constructions may be bad. When there is a problem, they may shift responsibility onto each other. Too much interweaving is a difficult problem facing the traditional data center.
7. The delivery period is often delayed. Among all the projects I have known, almost no project can be delivered on time. Almost all projects have been delayed.
To sum up, we desperately need to explore a new type of construction mode to overcome the preceding problems that exist in the process of data center construction.
Simplicity is both the beginning and the end
Since 2009, Tencent has tried to explore a new data center construction mode and has some new thoughts on the new data center architecture based on the current situation of China’s data center industry. Tencent mainly combined the construction, power distribution, cooling, automation, construction order, scale and granularity, and cost and business matching. It combined the aisle containment technology and in-row cooling technology which have been applied maturely with the innovative high-voltage direct current (HVDC) power supply technology and battery distribution technology. Besides, Tencent also unified the ports between units, between the micro-module and the infrastructure of a data center. It has summarized the philosophy of “simplicity is both the beginning and the end”.
The innovation Tencent has made in the data center micro-module is that it proposed “micro-modular data center”. By 2013, Tencent has completed the exploratory accumulation in the initial stage of micro-module practice and has started to prepare for large-scale practice of micro-modular data centers.
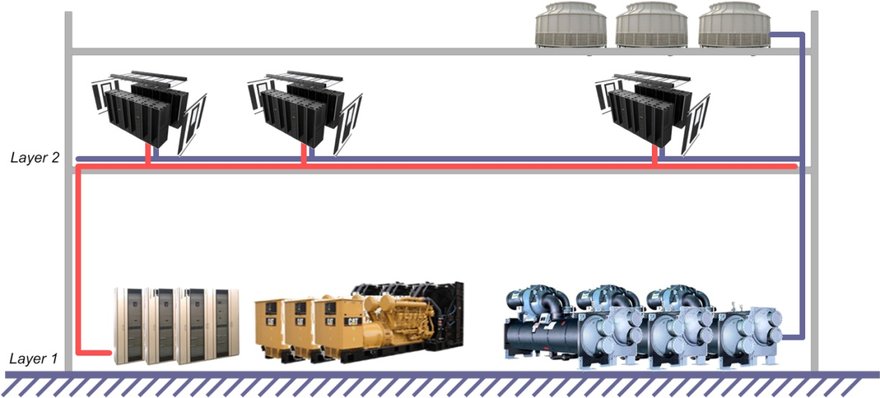
The ultimate goal of modular design is productization. Micro-module is a method of productizing data centers. Make the IT part in a data center as a standardized product. It is independent of data center infrastructure such as cooling, fire control, water, and electricity. Key components, such as in-row air conditioners, DC power, modular UPS, and batteries, are ordinary standardized products. They are highly commercialized, easy and flexible to configure at any time, and support online capacity expansion.
The structure of micro-module can adapt to the conditions of most factory buildings in China. The micro-module has no special requirements for buildings, and is easy to assemble, transform, and move. Each micro-module can be seen as a miniature data center which can operate independently and has the ability to restore itself.
Modular design includes power supply modular design and cooling modular design. However, if a module is formed by combining cabinets with aisle containment, while the large-capacity UPS or HVDC system is still used for supplying centralized power, and in-room air conditioners are used for central cooling in equipment rooms, this is not real modular design.
The real modular design turns the central large-capacity UPS or HVDC system into distributed small-capacity UPS or HVDC, and large-capacity in-room air conditioners used for central cooling into small-capacity in-row air conditioners. The small-capacity UPS or HVDC and in-row air conditioners are integrated with the cabinet aisle to form a micro-modular data center.
The whole micro-modular data center is a product, and can be connected to the outside over standard power supply ports, cooling source ports, and network ports. This is the real modular design. If possible, free cooling can be adopted as the cooling source. In this way, the cooling part of the equipment room is isolated from the large and complicated central air-conditioning cooling source system, which brings better modular effect.
Replacing old data centers can be expected soon
Tencent has proved that the micro-module solution is a successful attempt with its own practice.
- Construction CAPEX pressure: reduced by 10%
- OPEX pressure: reduced by 35%–40%, saving energy
- Data center adaptability to requirements: plug-and-play, order on demand, delivery on demand, and reduction of initial investments
- Coupling between building and IT planning: decoupled, module production and civil construction concurrently implemented to reduce the cycle
- Onsite quality: standardization and productization reducing the engineering workload and complexity
- Risk control: factory production strictly following a set of mature industrial control process
- Equipment room deployment cycle: four weeks covering from onsite installation to acceptance test
The successful practice of the micro-module has attracted lots of manufacturers to join, so that the micro-module R&D is intensified, some excellent micro-module products have appeared on the market, and the modular data center industry is flourishing. According to statistics, by the end of September 2015, the implemented micro-modules in mainland China have totaled 1100 sets (excluding Huawei), and more than 400,000 servers have been deployed, which grows more than twice as against 2014.The output value has reached more than 2 billion yuan.
By 2016, it is estimated that the micro-modules will total 1900 sets and the number of servers will exceed 700,000. Meanwhile, the industry has started to deepen, extract, and summarize the micro-module systemic technology requirements, with the aim to give a comprehensive standardized definition for the micro-module and realize productization to meet the industry development requirements.
With the gradual establishment and improvement of the industry standard, the micro-modular data center will become a mainstream.
Zhu Hua is the director of Technology Development Center for Tencent Data Centers.