Terms like next-generation factory automation and ‘Industry 4.0’ describe the impact 5G, the IoT, and artificial intelligence will have on operations like manufacturing and material handling. Declaring a fourth industrial revolution places this transition on par with the original steam powered machinery used to alleviate centuries of human toil, or the first electric assembly lines of the early 20th century.
The industrial IoT
The Internet of Things (IoT) is based on the addition of compact sensors and communication technology to almost any object or device so that information can be collected and shared more easily. Although this practice dates back more than a century, the advent of 5G introduces exponential connectivity and latency improvements that push IoT into uncharted territory.
The industrial internet of things (IIoT), supporting advanced factory automation, converts real-time data from robotics, equipment, tools and products into analytics and decisions that dramatically improve efficiency.
Factory automation and hyperscale
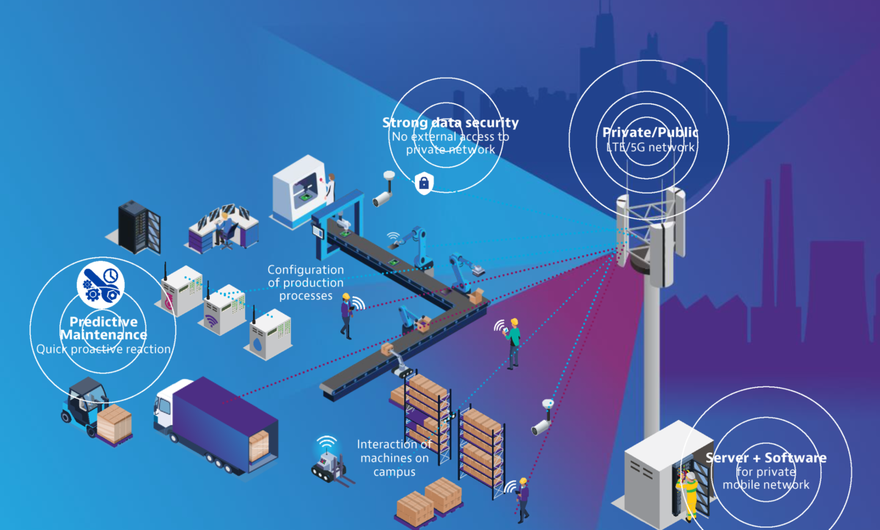
The guarded intellectual property and closed quarters of high-tech factories and distribution centers make them a perfect fit for private 5G networks and small cell technology. At the same time, smart factory data rates from 1-20 Gb/sec, ultra-reliable, low-latency communication (URLLC), and IoT connection density in the millions combine to make factory automation a demanding use case. Although private 5G networks can safeguard security and latency requirements, high-volume Industry 4.0 computing and data storage rely on hyperscale horsepower.
Data center software is essential for coordinating and analyzing IoT data, optimizing production processes, and determining predictive maintenance trigger points. Public cloud services are a scalable option for AI computing and big data storage that can be harmonized with the unique requirements of each industrial network. Encryption techniques alleviate the privacy and security concerns of factory operators partnering with hyperscalers.
Factory automation benefits
Improved productivity
First and foremost among next-generation factory automation benefits is the improved productivity that comes from continuous real-time monitoring and automated decision-making. Rather than waiting for humans to analyze and act on the wealth of available information, machine-to-machine (M2M) communication enables real-time data from multiple sources to be analyzed continuously. Advanced algorithms produce decisions that automatically correct, revise, or optimize processes. Errors, bottlenecks, and malfunctions that contribute to waste and reduce throughput are gradually eliminated through continuous improvement.
Predictive maintenance
What was once just a screwdriver is now an IIoT device continuously streaming information on torque, wear, and 3D position. Predictive maintenance processes analyze data from millions of tools, devices, and machines to determine precisely when calibration and maintenance are needed and what the service should include. Although sensors have collected industrial data for decades, the low latency and intelligence of 5G introduce a more dynamic maintenance loop where equipment breakdowns and excessive wear are all but eliminated. Hyperscale cloud computing power converts the sensory feedback into actionable maintenance schedules, work orders, and procurement plans.
Improved safety
Workplace safety contributes to ongoing employee satisfaction and retention. The tightly choreographed movement of parts, machines, and vehicles orchestrated by hyperscale artificial intelligence also considers the role of human operators as they interact with smart factory elements. Enhanced Industry 4.0 visibility translates into improved workplace safety as equipment degradation is detected in real time and workers are alerted to potential hazards. Accidents can be reported immediately with operations automatically paused while the proper response is organized.
Increased agility
Beyond the unprecedented factory awareness made possible by the IIoT, next-generation factory automation also enables production lines to be scaled up or down quickly, including new products that are added to the mix. Production changeovers in the “Industry 3.0” ecosystem involved manual, time-consuming adjustments to production layouts, purchase orders, and logistics. Hyperscale computing power offloads this analysis and automates the changeover process. This agility also extends to new product design, packaging, and inspection processes that are virtually modeled and optimized before they ever reach the floor.
Industry 5.0 and beyond
Throughout the history of factory automation, improved technology has led to higher levels of productivity, safety, and worker satisfaction, rather than the oft-predicted wholesale displacement of workers by machines. The electricity and computing power that marked previous transitions also led to similar skepticism. Much like the revolutions that preceded it, the melding of 5G, hyperscale computing, and factory automation will produce unlimited benefits and opportunities as efficiency soars and computers assume ownership of mundane and dangerous tasks.
Although the full impact of Industry 4.0 has yet to be felt, discussions and predictions surrounding the next foundational technology already persist. Breakthrough innovations ranging from augmented reality to cyborg operators could bring us closer to “Industry 5.0”. Despite calls for a return to a more human-centric industrial environment, it is likely that computer technology will remain at the heart of the discussion. Hyperscale data centers will continue to enable this progression as computing power and big data storage foster the next big thing.
By developing test solutions and expertise that bridge the gap between private 5G networks and hyperscale data centers, Viavi is lighting a path to efficient, reliable next generation factory automation. An interoperable portfolio of network testing, performance optimization, and service assurance tools support the most complex hybrid ecosystems. VIAVI solutions deliver unparalleled visibility into network operation and services at all stages of the lifecycle.